41. Flight Plan Route Description
This dialog allows you to create a flight plan from a route description string consisting of airport and navaid idents as generated or provided by various online services.
Click Load from Flight Plan to generate the route string from the currently loaded flight plan.
This will append and read the string on the top of the list.
The top of the dialog holds the route description input field, while the center half shows any messages, warnings or errors that occur during reading. The string is read automatically while entering it into the input field. The lower part provides a quick help.
41.1. Input Field
The upper input field is split into two sections. The top most can cover several lines and is is shown using bold text. This is the active section which is read and the results are shown in the output.
The lower text can be seen as a kind of a notepad, is displayed in gray color and is ignored for reading.
The two sections are separated by an empty line. You can copy and paste lines between the two sections using the context menu
or the keyboard shortcuts copy Ctrl+C, cut Ctrl+X and paste Ctrl+V.
All texts are saved on exit.
41.2. Reading
Little Navmap tries to use as much of the route as possible even if parts of the flight plan like waypoints or airways cannot be found or names are ambiguous. You will see warnings in the center output field if that is the case.
If a route covers a long distance and contains a waypoint name which is not unique, a wrong waypoint might be added to the flight plan. Correct or remove this waypoint manually in the Flight Plan Table using the Context Menu Flight Plan.
Many waypoints and airways will not be found if route descriptions from the latest AIRAC sources are used together with the old FSX, P3D or MSFS stock data. It is recommended to use a navigation data update for the stock scenery or Little Navmap when reading route descriptions from online sources like RouteFinder, Online Flight Planner, SimBrief or SkyVector.
If a navdata update is not an option, pick the online service’s AIRAC cycle that is closest to the cycle the navigation data of your flight simulator is based on.
Note that even flight plans calculated in Little Navmap cannot be converted back exactly in some cases. This happens due to navaid ambiguities like NDB and VOR stations having the same names or errors in the source data.
The cruise altitude is used to create the flight plan, if given. Otherwise the cruise altitude is automatically determined by the flight plan type (IFR or VFR) and the minimum altitude of the used airway segments.
The cruise speed is ignored when reading and produces a warning if found since it is taken from the aircraft performance. Generating a description from a present flight plan uses the cruise speed from the loaded aircraft performance file ( Aircraft Performance) and the cruise altitude as set in Cruise altitude.
Note that you can modify the flight plan in parallel on the map or in the flight plan table. Move
the Flight Plan Route Description aside to do so.
You have to transfer the plan to the dialog by clicking Load from Flight Plan after doing changes in the background.
Click Create Flight Plan before doing changes on the map or in the flight plan table.
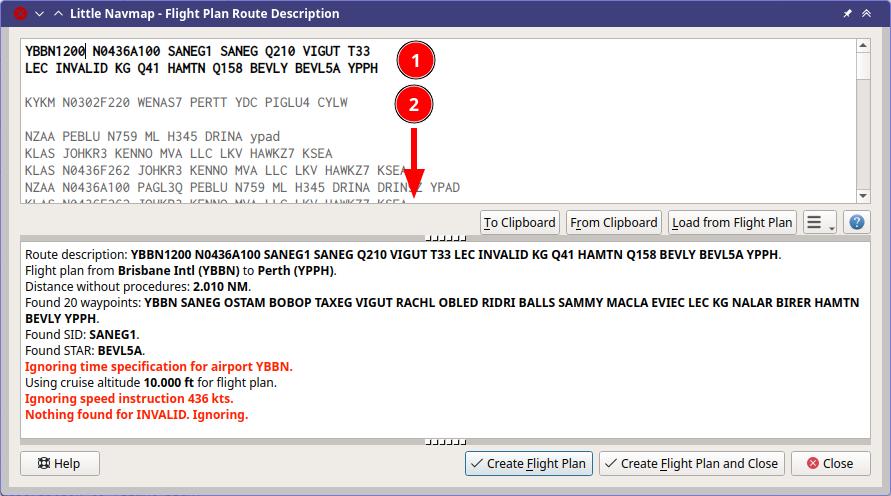
A route description (1) (bold top section) that was read successfully with
a few warnings about ignored elements. The waypoint INVALID could not be
found. Altitude, SID and STAR were recognized.
More inactive route descriptions are stored below (2).
41.4. Airport idents
ICAO, FAA, IATA and local codes are shown and the internal ident is avoided for display if possible. Note that IATA codes are only read for departure and destination since they can be easily confused with navaids en-route.
X-Plane internal codes like XPA000B are recognized despite being avoided for display.
41.5. Format
The route description has to follow the format rules below:
FROM[ETD] [SPEEDALT] [SIDTRANS] [ENROUTE] [STARTRANS] TO[ETA] [ALTERNATES]
All elements in square brackets are optional.
FROMandTO: These are the required 3 or 4 letter idents for departure and destination airports. Departure timeETDor arrival timeETAis ignored. Examples:KEAT,CYPU,S16.ALTERNATES: Alternate airports are optional and are added to the flight plan when reading depending on the optionRead trailing Airports as Alternatesas described above.SPEEDALT: An optional entry that contains the cruise speed and altitude. See below for a details. Speed is ignored when reading since it is part of the aircraft performance profile.ENROUTE: This is a list of eitherWAYPOINTor anAIRWAYWAYPOINTforming the actual flight plan. The first entry has to be an airport, waypoint, VOR or NDB.WAYPOINT: A waypoint, VOR, NDB, airport or user defined coordinates. See below for a details about coordinates. A waypoint can be prefixed withDCTto indicate a direct connection not using an airway. Waypoints can be suffixed with an optional/SPEEDALTvalue although this is ignored. Examples:TAU,BOMBI,AST,CL,EDDF.AIRWAYWAYPOINT: Airway and end waypoint on the airway separated by a space. Examples:V495 CONDI,V338 YVR,V330 TRENA.SIDTRANS: Either the wordSIDor real SID, STAR and transition names where the optional transition is separated by a dot.or a space ``. The generic keyword ``SIDcreates a direct connection to the en-route part. Examples:RDHK2.HOLLE,OHIO3 LFK,RDHK2,OHIO3.SIDTRANS: Either the wordSIDor real SID and transition names where the optional transition is separated by a dot.or a space ``. The generic keyword ``SIDcreates a direct connection to the en-route part. Examples:RDHK2.HOLLE,OHIO3 LFK,RDHK2,OHIO3.STARTRANSis either the wordSTARor a read STAR and an optional transition which can be given asSTAR.TRANS,STAR TRANS,TRANS.STARorTRANS STAR. The generic keywordSTARcreates a direct connection from the en-route part to the airport.
41.5.1. Features not supported
ETD and ETA: Four digit departure and arrival time attached to
the airport or waypoint ident are ignored.
WAYPOINT.SPEEDALT: For example BOMBI/N0090A060. Altitude changes
at waypoints are not supported and ignored when reading.
Further extensions like runway and approaches are not supported.
41.5.2. Alternates
Example when reading Read trailing Airports as Alternates enabled:
KPWA N0169F190 MUDDE3 ATOKA J25 FUZ J33 CRIED J50 LFK BAYYY3.SJI KHOU KCLL KVCTKPWA ATOKA J25 FUZ J33 CRIED J50 LFK KHOU KCLL KVCT
KHOU is read as destination, KCLL and KVCT are alternates
for both examples.
Example when reading Read trailing Airports as Alternates disabled:
KPWA N0169F190 MUDDE3 ATOKA J25 FUZ J33 CRIED J50 LFK BAYYY3.SJI KHOU KCLL KVCT
Not valid. Error message BAYYY3.SJI not found printed. KVCT is
read as destination, KHOU and KCLL are intermediate waypoints.
KPWA ATOKA J25 FUZ J33 CRIED J50 LFK KHOU KCLL KVCT
KVCT is read as destination, KHOU and KCLL are intermediate
waypoints.
41.5.3. Speed and Altitude
Cruising ground speed and cruising level not separated by a space.
Speed is prefixed with:
K: Kilometers per hour followed by a four digit value.N: Knots followed by a four digit value.M: Mach followed by a three digit value. The mach value is converted to knots ground speed assuming standard atmosphere conditions at the given flight altitude.
Altitude is prefixed with:
F:Flight level in three digits.S: Metric flight level in three digits of tens of meters.A: Altitude in hundreds of feet in three digits.M: Altitude in tens of meter in four digits.
Examples:
N0410F310 410 knots at flight level 310.
M071F320 Mach 0.71 at flight level 320.
K0790M0710 790 kilometers per hour at 7,100 meters.
41.5.4. Coordinates
Coordinates can be supplied in different formats:
Degrees only (7 characters): Two digits and north/south indicator plus three digits and east/west indicator.
Example: 51N010E
Degrees and minutes (11 characters): Two digits degrees, two digits for minutes and north/south indicator. Then three digits for degrees, two digits for minutes and east/west indicator.
Example: 4010N03822W.
Degrees, minutes and seconds (15 characters): Two digits degrees, two digits for minutes, two digits for seconds and north/south indicator. Then three digits for degrees, two digits for minutes, two digits for seconds and east/west indicator. This format is used by SkyVector for example.
Example: 481200N0112842E.
ARINC 424 Code Convention: All full degree waypoints either a part of the navigation database or not.
Examples: 57N30 (N57 W130) or 5730S (S57 W030).
North Atlantic track points (NAT). Two digits degrees north and two
digits degrees west followed by character N.
Example: 5010N.
Coordinate waypoint pairs with degrees and minutes as above and prefixed with north/south and east/west indicator.
Examples: N4200 W02000 or N4200/W02000.
Garmin GFP format (13 characters) north/south indicator, two digits degrees, three digits for minutes by 10. Then east/west indicator, three digits degrees, three digits minutes by 10. This format is used by the Flight1 GTN 650/750.
Example: N48194W123096
41.6. Flight Plan Description Examples
Frankfurt Main (EDDF) to Fiumicino (LIRF):
Direct connection:
EDDF LIRF or EDDF DCT LIRF.
VOR to VOR:
EDDF FRD KPT BOA CMP LIRF.
Same as above with departure time ( ETD ) and arrival time
( ETA ) which both will be ignored:
EDDF1200 FRD KPT BOA CMP LIRF1300.
Same as above on flight level 310 at 410 knots:
EDDF N0410F310 DCT FRD DCT KPT DCT BOA DCT CMP DCT LIRF
Using Jet airways:
EDDF ASKIK T844 KOVAN UL608 TEDGO UL607 UTABA UM738 NATAG Y740 LORLO M738 AMTEL M727 TAQ LIRF
Same as above on flight level 310 at mach 0.71 with an additional
speed and altitude at NATAG which will be ignored:
EDDF M071F310 SID ASKIK T844 KOVAN UL608 TEDGO UL607 UTABA UM738 NATAG/M069F350 Y740 LORLO M738 AMTEL M727 TAQ STAR LIRF
User defined waypoints with degree/minute notation and an alternate
airport LIRE :
EDDF N0174F255 4732N00950E 4627N01019E 4450N01103E LIRF LIRE
Flight plan using SID and STAR procedures with transitions:
KPWA RDHK2.HOLLE ATOKA J25 FUZ J33 CRIED J50 LFK OHIO3.LFK KHOU
Flight plan using the generic SID and STAR keywords:
KPWA SID ATOKA J25 FUZ J33 CRIED J50 LFK STAR KHOU
Flight plan using SID and STAR procedures with transitions and two alternate airports:
KPWA N0169F190 MUDDE3 ATOKA J25 FUZ J33 CRIED J50 LFK BAYYY3.SJI KHOU KCLL KVCT